Genetic and gene expression heterogeneity is an essential hallmark of many tumors, allowing the cancer to evolve and to develop resistance to treatment. Currently, the most commonly used data types for studying such heterogeneity are bulk tumor/normal whole-genome or whole-exome sequencing (WGS, WES); and single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), respectively. However, tools are currently lacking to link genomic tumor subclonality with transcriptomic heterogeneity by integrating genomic and single-cell transcriptomic data collected from the same tumor.
To address this gap, researchers at the University of Utah have developed scBayes, a Bayesian probabilistic framework that uses tumor subclonal structure inferred from bulk DNA sequencing data to determine the subclonal identity of cells from single-cell gene expression (scRNA-seq) measurements. Grouping together cells representing the same genetically defined tumor subclones allows comparison of gene expression across different subclones, or investigation of gene expression changes within the same subclone across time (i.e., progression, treatment response, or relapse) or space (i.e., at multiple metastatic sites and organs). The researchers used simulated data sets, in silico synthetic data sets, as well as biological data sets generated from cancer samples to extensively characterize and validate the performance of their method, as well as to show improvements over existing methods. The researchers show the validity and utility of their approach by applying it to published data sets and recapitulating the findings, as well as arriving at novel insights into cancer subclonal expression behavior in our own data sets. They further show that their method is applicable to a wide range of single-cell sequencing technologies including single-cell DNA sequencing as well as Smart-seq and 10x Genomics scRNA-seq protocols.
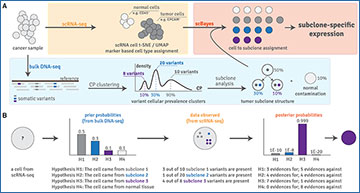
Overview of the scBayes algorithm
(A) The scBayes algorithm combines single-cell RNA sequencing-based transcriptomic analysis (shaded in yellow) with bulk DNA sequencing-based genetic subclone analysis (shaded in blue) to derive subclone-specific expression profiles (shaded in red) via assigning each cell a tumor subclone identity. Cells representing normal cell contamination are also assigned. CP stands for cellular prevalence. (B) Simplified overview of our probabilistic model. For a given cell, scBayes evaluates the Bayesian posterior probabilities that the cell represents each of the genetic subclones while taking evolution into consideration (e.g., for H3, both variants of subclone 1 and subclone 3 are considered positive evidences because subclone 3 is the descendent of subclone 1). The cell is assigned to the subclone that maximizes the posterior probability, and meets a minimum probability threshold. See Methods for a complete description of our statistics mode
Availability – The scBayes software is open source, and available as Supplemental Code 2 and at GitLab (https://gitlab.com/yiq/scbayes).
Qiao Y, Huang X, Moos PJ, Ahmann JM, Pomicter AD, Deininger MW, Byrd JC, Woyach JA, Stephens DM, Marth GT. (2024) A Bayesian framework to study tumor subclone-specific expression by combining bulk DNA and single-cell RNA sequencing data. Genome Res [Epub ahead of print]. [abstract]