Cell-free RNAs (cfRNAs) offer an opportunity to detect diseases from a transcriptomic perspective, however, existing techniques have fallen short in generating a comprehensive cell-free transcriptome profile. Researchers at Shenzhen University have developed a sensitive library preparation method that is robust down to 100 µl input plasma to analyze cfRNAs independent of their 5’-end modifications. The researchers show that it outperforms adapter ligation-based method in detecting a greater number of cfRNA species. They perform transcriptome-wide characterizations in 165 lung cancer, 30 breast cancer, 37 colorectal cancer, 55 gastric cancer, 15 liver cancer, and 133 cancer-free participants and demonstrate its ability to identify transcriptomic changes occurring in early-stage tumors. The researchers also leverage machine learning analyses on the differentially expressed cfRNA signatures and reveal their robust performance in cancer detection and classification. This work sets the stage for in-depth study of the cfRNA repertoire and highlights the value of cfRNAs as cancer biomarkers in clinical applications.
Technology optimizations of SLiPiR-seq
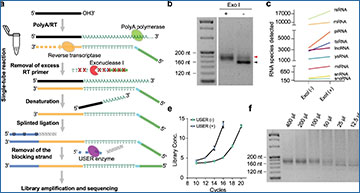
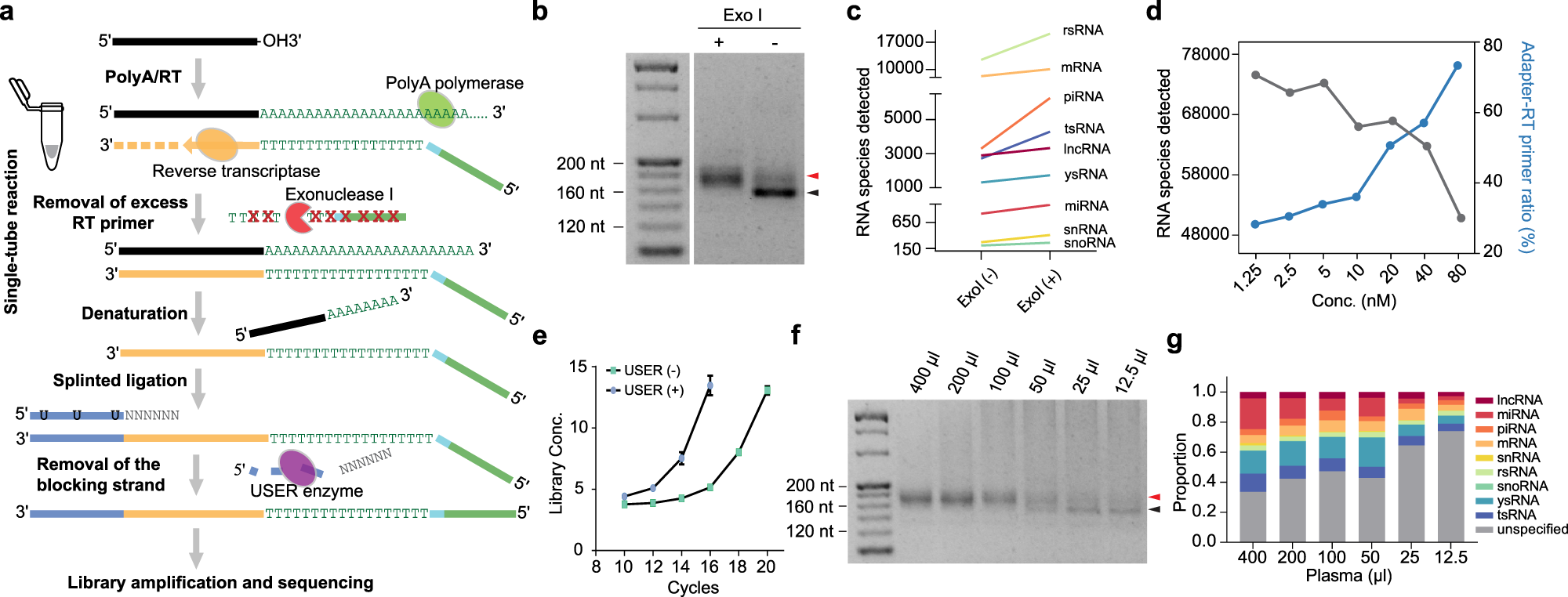
a Schematic representation of the SLiPiR-seq workflow. b Gel electrophoresis showing the effect of ExoI treatment on the final library size. Black arrow indicates the library size derived from the ligation between RT primer and adapter. Red arrow indicates the correct cfRNA library size. c Effect of ExoI treatment on the number of cfRNA species detected (RPM > 0) from nine RNA types. d Effect of different concentration of RT primer (from 1.25 nM to 80 nM) on the number of cfRNA species detected and adapter-RT primer reads ratio. e Effect of USER enzyme treatment on library amplification efficiency. Library concentrations (ng/µl) of different amplification cycles are shown. Points represent mean of three technical replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviation (SD). f Gel electrophoresis showing the size of final libraries produced by different starting input volumes of plasma (from 12.5 µl to 400 µl). g Proportion of different kinds of cfRNAs across different starting input volumes of plasma. For all graphs, N = 3 technical replicates were performed for all conditions, and the mean of the replicates was calculated. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Wang J, Huang J, Hu Y, Guo Q, Zhang S, Tian J, Niu Y, Ji L, Xu Y, Tang P, He Y, Wang Y, Zhang S, Yang H, Kang K, Chen X, Li X, Yang M, Gou D. (2024) Terminal modifications independent cell-free RNA sequencing enables sensitive early cancer detection and classification. Nat Commun 15(1):156. [article]