Alternative polyadenylation (APA) plays an important role in posttranscriptional gene regulation such as transcript stability and translation efficiency. However, our knowledge about APA dynamics at the single-cell level is largely unexplored. Researchers at Zhengzhou University have developed single-cell polyadenylation sequencing (scPolyA-seq), a strand-specific approach for sequencing the 3′ end of transcripts, to investigate the landscape of APA at the single-cell level. By analyzing several cell lines, the researchers found many genes using multiple polyA sites in bulk data are prone to use only one polyA site in each single cell. Interestingly, cell cycle genes were significantly enriched in genes with high variation in polyA site usages. Furthermore, the 414 genes showing a polyA site usage switch after cell synchronization enriched cell cycle genes, while the differentially expressed genes after cell synchronization did not enrich cell cycle genes. The researchers further identified 812 genes showing polyA site usage changes between neighboring cell cycles, which were grouped into six clusters, with cell phase-specific functional categories enriched in each cluster. Deletion of one polyA site in MSL1 and SCCPDH results in slower and faster cell cycle progression, respectively, supporting polyA site usage switch played an important role in cell cycle. These results indicate that APA is an important layer for cell cycle regulation.
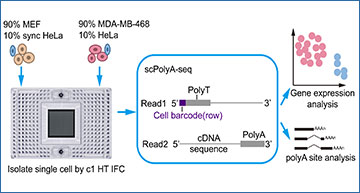
scPolyA-seq and scheme of this study
(A) Scheme of scPolyA-seq. The 3’end of mRNA is captured and sequenced. Read 1 carry cell barcode, while Read 2 may contain polyA sites and sequences nearby. Read 2 is used for identifying the PolyA sites and calculating gene expression. (B) Experiment design of this study. Cell suspensions of MDA-MB-468 and MEF (both mixed 10% HeLa cells) are loaded into two independent inlets of C1 HT integrated fluidics circuit (IFC), thus up to 400 cells can be captured for each cell suspension. (C) Pearson correlation of gene expression between pooled scRNA-seq and bulk RNA-seq data of MDA-MB-468. (D) scPolyA-seq generates much more reads and detects more genes for each cell compared with 10x scRNA-seq. (E) Reads from scPolyA-seq showed the sharpest peak at 3’end of each gene, compared with 10x scRNA-seq and Smart-seq2. (F) UMAP plot of the 3 human cell line subpopulations, namely MDA-MB-468, normal HeLa and synchronized HeLa. (G) Heatmap of cell subpopulation specific genes.
Wang J, Chen W, Yue W, Hou W, Rao F, Zhong H, Qi Y, Hong N, Ni T, Jin W. (2022) Comprehensive mapping of alternative polyadenylation site usage and its dynamics at single-cell resolution. PNAS 119(49):e2113504119. [abstract]