DNA and RNA sequencing are widely used techniques to investigate genomic modifications and gene expression. The costs for sequencing dropped dramatically in the last decade. However, due to material and labor intense steps, the sample preparation costs could not keep up with that pace. About 80% of the total costs occur prior to sequencing during DNA/RNA extraction, enrichment steps and subsequent library preparation.
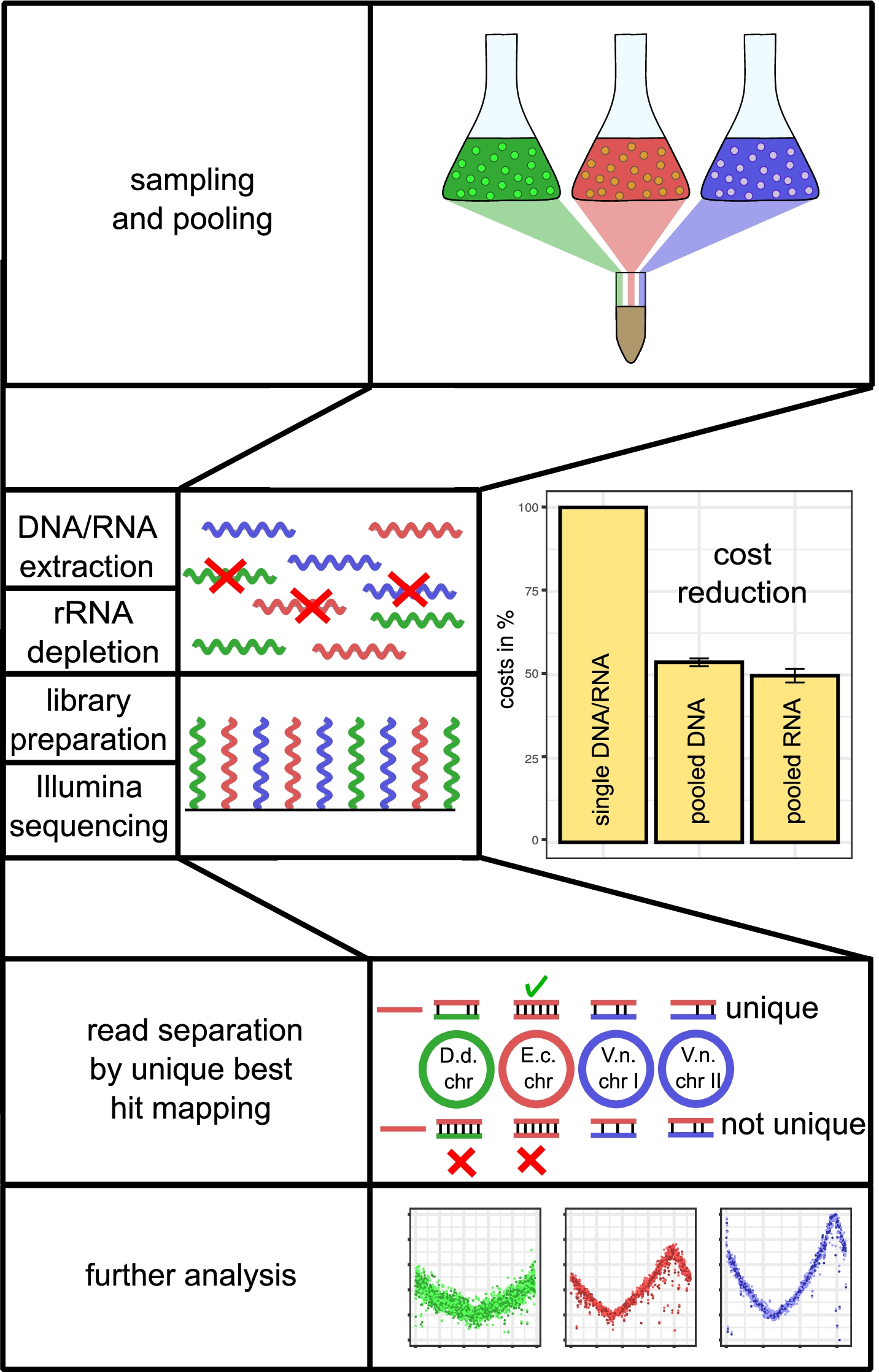
Researchers at Philipps Universität Marburg have now investigated the potential of pooling different organisms samples prior to DNA/RNA extraction to significantly reduce costs in preparative steps. Similar to the common procedure of ligated DNA tags to pool (c)DNA samples, sequence diversity of different organisms intrinsically provide unique sequences that allow separation of reads after sequencing. With this approach, sample pooling can occur before DNA/RNA isolation and library preparation. The researchers show that pooled sequencing of three related bacterial organisms is possible without loss of data quality at a cost reduction of approx. 50% in DNA- and RNA-seq approaches. Furthermore, they show that this approach is highly efficient down to the level of a shared genus and is, therefore, widely applicable in sequencing facilities and companies with diverse sample pools.
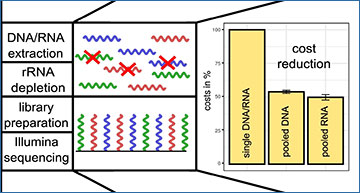
Pooling workflow
By pooling samples of different species, costs can be significantly reduced in DNA/RNA extraction, rRNA depletion and library preparation and sequencing. Costs for single samples are set to 100%. Costs of three companies for pooled samples are relative to single sample costs for DNA-seq and RNA-seq. Error bars indicate standard deviation of costs
Teufel M, Sobetzko P. (2022) Reducing costs for DNA and RNA sequencing by sample pooling using a metagenomic approach. BMC Genomics 23(1):613. [article]