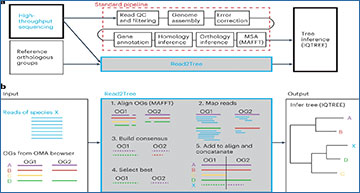
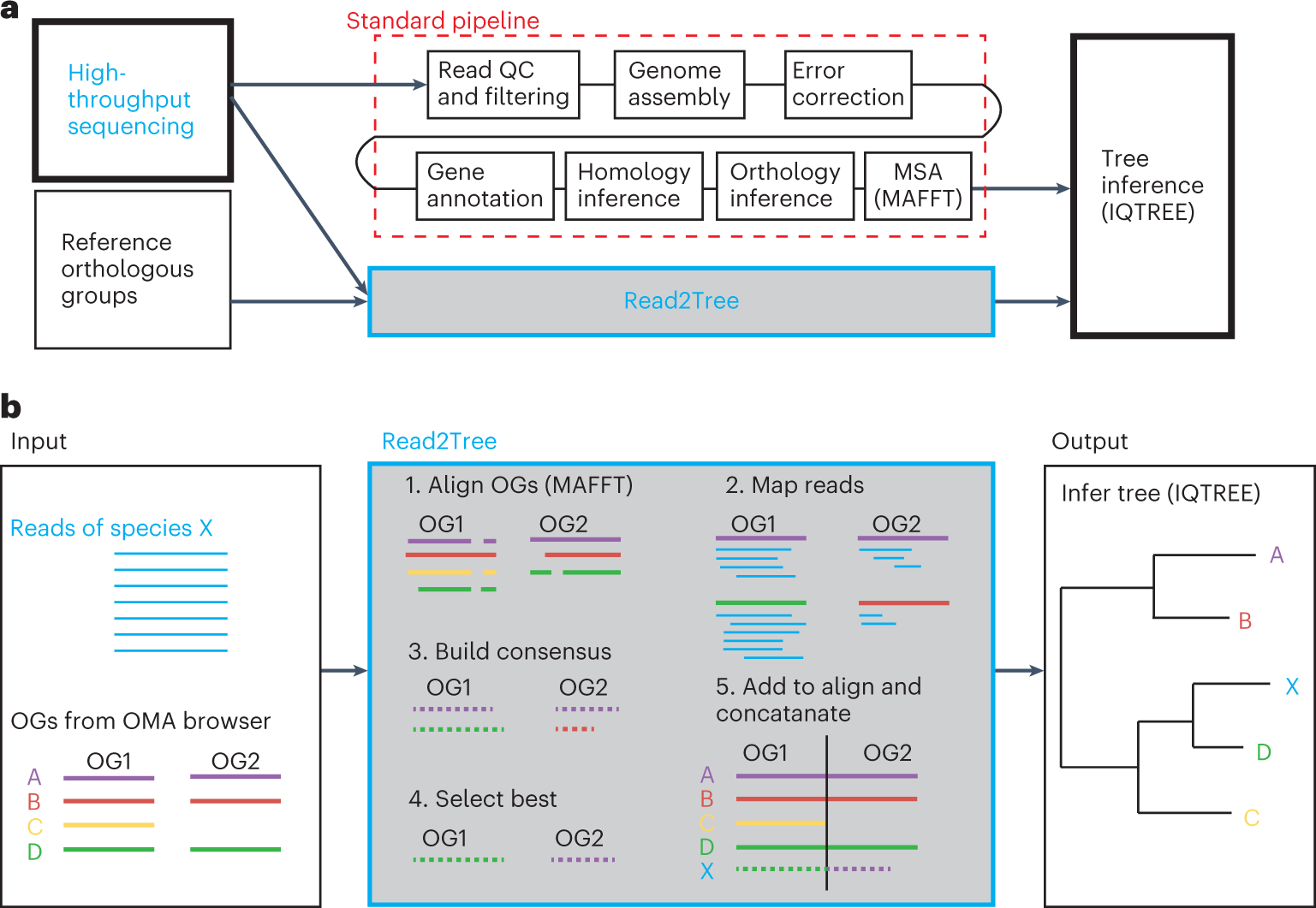
Current methods for inference of phylogenetic trees require running complex pipelines at substantial computational and labor costs, with additional constraints in sequencing coverage, assembly and annotation quality, especially for large datasets. To overcome these challenges, a team led by researchers at the University of Lausanne present Read2Tree, which directly processes raw sequencing reads into groups of corresponding genes and bypasses traditional steps in phylogeny inference, such as genome assembly, annotation and all-versus-all sequence comparisons, while retaining accuracy. In a benchmark encompassing a broad variety of datasets, Read2Tree is 10-100 times faster than assembly-based approaches and in most cases more accurate-the exception being when sequencing coverage is high and reference species very distant. To illustrate the broad applicability of the tool, the researchers reconstruct a yeast tree of life of 435 species spanning 590 million years of evolution. They also apply Read2Tree to >10,000 Coronaviridae samples, accurately classifying highly diverse animal samples and near-identical severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 sequences on a single tree. The speed, accuracy and versatility of Read2Tree enable comparative genomics at scale.
Strategy and pipeline explanation
a, Read2Tree aims at side stepping many time-intensive and costly pipeline steps to obtain a phylogenetic tree when using many species, therefore going from read to tree. b, Overview of the Read2Tree pipeline.
Availability – The source code for Read2Tree is available under an MIT open-source license at https://github.com/DessimozLab/read2tree
Dylus D, Altenhoff A, Majidian S, Sedlazeck FJ, Dessimoz C. (2023) Inference of phylogenetic trees directly from raw sequencing reads using Read2Tree. Nat Biotechnol [Epub ahead of print]. [article]