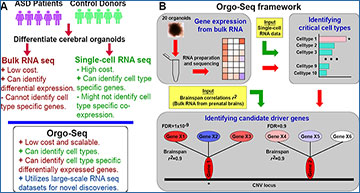
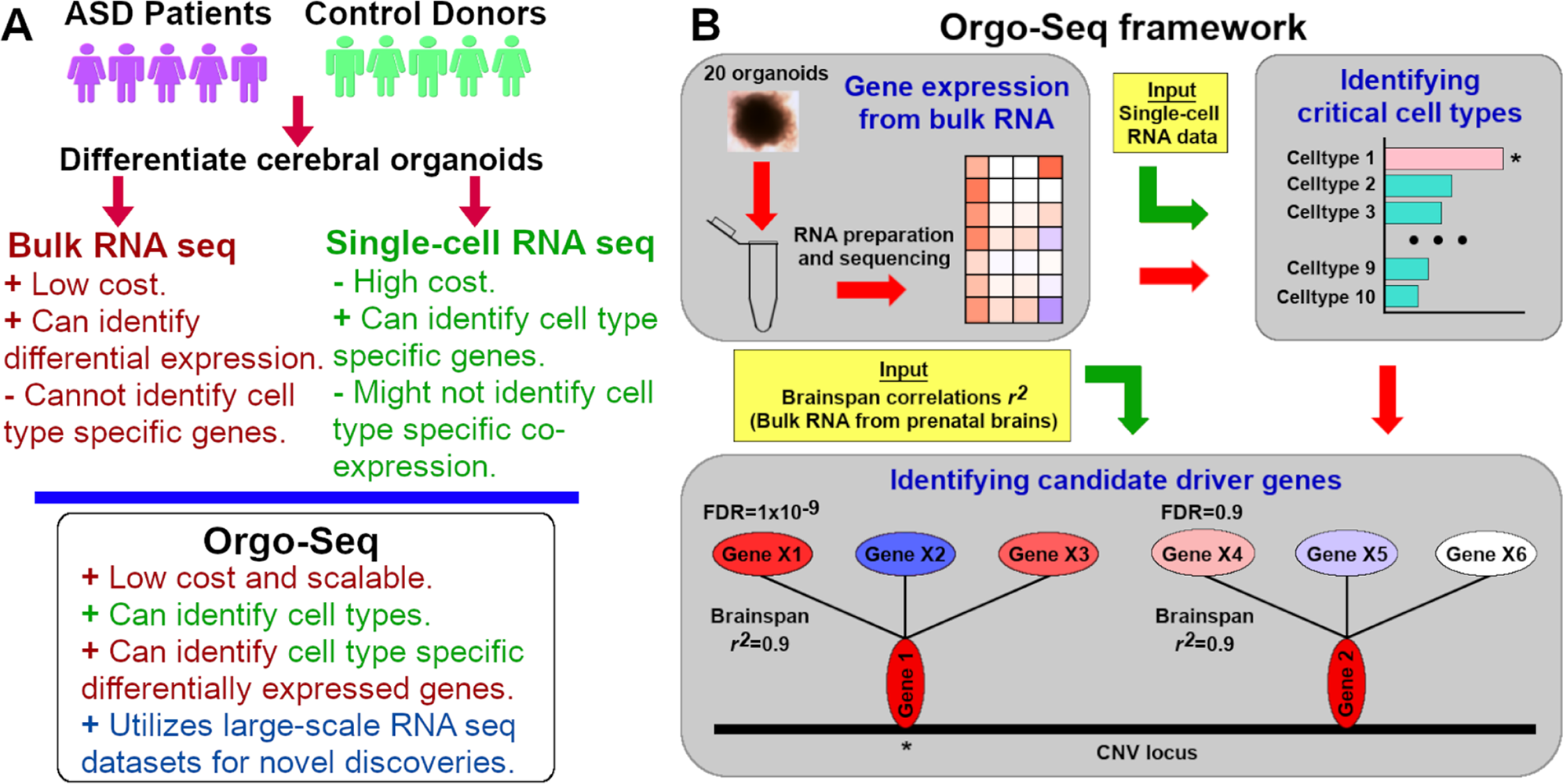
Cerebral organoids can be used to gain insights into cell type specific processes perturbed by genetic variants associated with neuropsychiatric disorders. However, robust and scalable phenotyping of organoids remains challenging. A team led by researchers at University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School performed RNA sequencing on 71 samples comprising 1,420 cerebral organoids from 25 donors, and describe a framework (Orgo-Seq) to integrate bulk RNA and single-cell RNA sequence data. The researchers applied Orgo-Seq to 16p11.2 deletions and 15q11–13 duplications, two loci associated with autism spectrum disorder, to identify immature neurons and intermediate progenitor cells as critical cell types for 16p11.2 deletions. They further applied Orgo-Seq to identify cell type-specific driver genes. This work presents a quantitative phenotyping framework to integrate multi-transcriptomic datasets for the identification of cell types and cell type-specific co-expressed driver genes associated with neuropsychiatric disorders.
Orgo-Seq framework to identify cell type-specific co-expressed driver genes
A Figure illustrating the strengths and weaknesses of bRNA-seq and scRNA-seq, and what Orgo-Seq can achieve by integrating both types of datasets. B A schematic of the Orgo-Seq framework to integrate bRNA-seq data from patient-derived brain organoids with scRNA-seq data from control brain organoids, for the discovery of critical cell types and cell type-specific driver genes.
Lim ET, Chan Y, Dawes P et al. (2022) Orgo-Seq integrates single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data to identify cell type specific-driver genes associated with autism spectrum disorder. Nat Commun [Epub ahead of print]. [article]