Alternative splicing is an important source of heterogeneity underlying gene expression between individual cells but remains an understudied area due to the paucity of computational tools to analyze splicing dynamics at single-cell resolution. Researchers at the University of Oxford have developed MARVEL, a comprehensive R package for single-cell splicing analysis applicable to RNA sequencing generated from the plate- and droplet-based methods. The researchers performed extensive benchmarking of MARVEL against available tools and demonstrated its utility by analyzing multiple publicly available datasets in diverse cell types, including in disease. MARVEL enables systematic and integrated splicing and gene expression analysis of single cells to characterize the splicing landscape and reveal biological insights.
MARVEL workflow for single-cell alternative splicing analysis
in RNA-sequencing dataset generated from plate-based methods
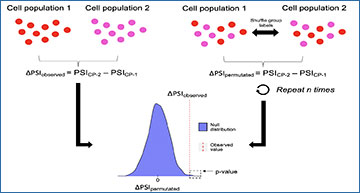
(A–C) Workflow for pre-processing of splicing and gene expression data by MARVEL. (A) Input files required by MARVEL include splice junction count and normalized gene expression matrix, alternative splicing events, and gene and sample metadata. (B) Only alternative splicing events supported by at least 10 splice junction reads are retained. (C) The PSI values of the confident alternative splicing events identified in (B) are computed for main exon-level alternative splicing event types. PSI values are calculated as the total number of reads supporting the alternative exons (pink) divided by the total number of reads supporting both alternative exons and constitutive exons (black). (D–G) Downstream analyses using computed PSI and gene expression values. (D) Dimension reduction analysis using differentially expressed genes (left), PSI values (middle), and PSI values of non-differentially expressed genes (right). (E) The assignment of PSI distributions into seven modalities (as indicated by colors) and the bimodal classification adjustment to reduce false bimodal classification. (F) Differential splicing and gene expression analysis and characterization of the alternative splicing in different modality changes or relative to gene expression changes across different cell populations. (G) Pathway enrichment analysis of differentially spliced genes and NMD prediction of alternative splicing events to understand the functional consequences of differential alternative splicing events. Genes subjected to NMD are visualized on the volcano plot generated from differential gene expression analysis.
Availability – MARVEL is available on the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN): https://cloud.r-project.org/web/packages/MARVEL/index.html.
Wen WX, Mead AJ, Thongjuea S. (2023) MARVEL: an integrated alternative splicing analysis platform for single-cell RNA sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res [Epub ahead of print]. [article]