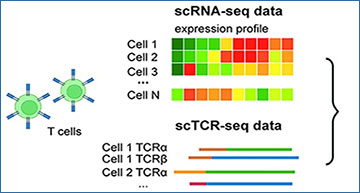
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data has been widely used for cell trajectory inference, with the assumption that cells with similar expression profiles share the same differentiation state. However, the inferred trajectory may not reveal clonal differentiation heterogeneity among T cell clones. Single-cell T cell receptor sequencing (scTCR-seq) data provides invaluable insights into the clonal relationship among cells, yet it lacks functional characteristics. Therefore, scRNA-seq and scTCR-seq data complement each other in improving trajectory inference, where a reliable computational tool is still missing.
Researchers at The Ohio State University have developed LRT, a computational framework for the integrative analysis of scTCR-seq and scRNA-seq data to explore clonal differentiation trajectory heterogeneity. Specifically, LRT uses the transcriptomics information from scRNA-seq data to construct overall cell trajectories and then utilizes both the TCR sequence information and phenotype information to identify clonotype clusters with distinct differentiation biasedness. LRT provides a comprehensive analysis workflow, including preprocessing, cell trajectory inference, clonotype clustering, trajectory biasedness evaluation, and clonotype cluster characterization. The researchers illustrate its utility using scRNA-seq and scTCR-seq data of CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells with acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. These analyses identified several clonotype clusters with distinct skewed distribution along the differentiation path, which cannot be revealed solely based on scRNA-seq data. Clones from different clonotype clusters exhibited diverse expansion capability, V-J gene usage pattern and CDR3 motifs.
The framework of LRT
(A) The preprocessed scRNA-seq and scTCR-seq data are integrated based on cell barcodes matching. (B) Cell trajectories are first obtained using the Slingshot algorithm. (C) Clonotypes with similar cell cluster composition are grouped using the Dirichlet multinomial mixtures (DMM) model. (D) For each clonotype cluster, the distributional bias of clones along the trajectories is evaluated via permutation tests. The repertoire is characterized in terms of clonal expansion and diversity, the top-ranked clonotypes, and V and J gene usage patterns, among others.
Availability – The LRT framework was implemented as an R package ‘LRT’, and it is now publicly accessible at https://github.com/JuanXie19/LRT. In addition, it provides two Shiny apps ‘shinyClone’ and ‘shinyClust’ that allow users to interactively explore distributions of clonotypes, conduct repertoire analysis, implement clustering of clonotypes, trajectory biasedness evaluation, and clonotype cluster characterization.
Xie J, Jeon H, Xin G, Ma Q, Chung D (2023) LRT: Integrative analysis of scRNA-seq and scTCR-seq data to investigate clonal differentiation heterogeneity. PLoS Comput Biol 19(7): e1011300. [article]