Understanding genetic mutations is crucial for various applications, from diagnosing diseases to unraveling the complexities of gene expression. While most mutation analysis is traditionally performed at the DNA level, there is a growing need for techniques capable of analyzing mutations directly in RNA. This is especially important for applications such as transcriptional mutagenesis, RNA editing, and gene expression analysis. Researchers from the University of Gothenburg have devised a novel approach that combines reverse transcription with digital DNA sequencing to enable highly accurate and sensitive RNA mutation analysis, opening new doors for research and clinical applications.
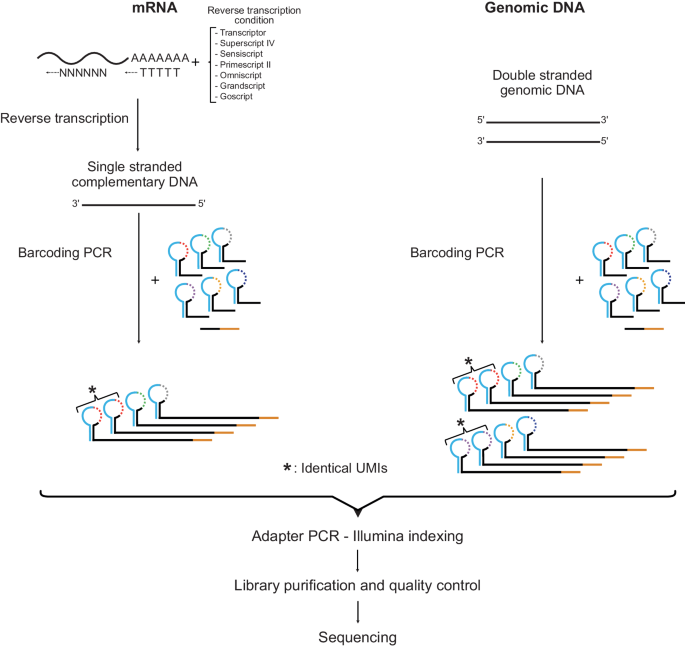
The SiMSen-Seq workflow for RNA and DNA analysis, respectively
Complementary DNA is single-stranded, while genomic DNA is double-stranded, resulting in three and six different UMIs, respectively. One-third of the reaction volume of barcoding PCR is loaded into the adapter PCR. The tested RT conditions are shown.
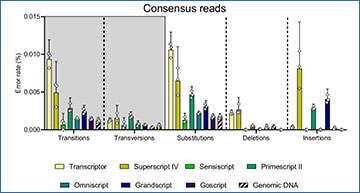
Evaluating Reverse Transcription Conditions
The study evaluated seven different reverse transcription conditions using multiplexed assays to assess yield, reproducibility, dynamic range, and error correction rate. Results showed substantial variation in yield, reproducibility, and error rate among the different conditions, with up to a 9.9-fold difference in yield between the best and worst performing condition.
Achieving High Accuracy in RNA Sequencing
By optimizing reverse transcription conditions, researchers were able to achieve error rates similar to DNA sequencing for RNA analysis. This breakthrough enables the detection of mutant allele frequencies as low as 0.1% at the RNA level, allowing for ultra-sensitive mutation analysis directly in RNA samples.
Applications in Cancer Research and Liquid Biopsies
The potential of digital RNA sequencing was further demonstrated in cancer research, where mutations were detected at both DNA and RNA levels in tumor tissue using a breast cancer panel. Additionally, the technique was successfully applied to liquid biopsies, analyzing cell-free gene transcripts, thereby paving the way for non-invasive diagnostics and monitoring of disease progression.
The development of digital RNA sequencing represents a significant advancement in mutation analysis, offering a highly sensitive and accurate method for studying mutations directly in RNA. This breakthrough technique holds immense potential for various applications in basic research and clinical settings, including cancer research, personalized medicine, and liquid biopsy analysis. As researchers continue to explore the capabilities of digital RNA sequencing, we can expect further innovations that will revolutionize our understanding of RNA biology and disease mechanisms.
Luna Santamaría M, Andersson D, Parris TZ, Helou K, Österlund T, Ståhlberg A. (2024) Digital RNA sequencing using unique molecular identifiers enables ultrasensitive RNA mutation analysis. Commun Biol 7(1):249. [article].