Single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) presents an opportunity to deconstruct cellular networks but is limited by the loss of biological information, including in vivo cellular states and phospho-signaling. Researchers from the University of Alabama at Birmingham present fixation before dissociation using a deep eutectic solvent (DES), which preserves multiple domains of in vivo biological data, including morphology, RNA, proteins, and post-translational modifications. In scRNA-seq of viable versus DES bone marrow, dissociation induced global stress responses, immune and stromal cell activation, and loss of highly sensitive cell populations, which were prevented with DES. Further, the researchers introduce a validated and flexible method for performing intracellular CITE-seq in DES-fixed cells. Leveraging this approach during Th17 T cell stimulation allowed the simultaneous quantification of transcriptomes and four phosphorylated proteins, leading to the identification of a hyperactivated state in p-ERK/p-FOS double positive cells, which they experimentally validated. These researchers anticipate that DES-based fixatives will allow the accurate reconstruction of in vivo cellular networks and uncover cooperativity amongst intracellular pathways.
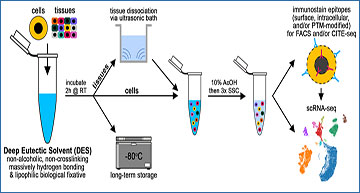
Schematic overview of fixation before dissociation using deep eutectic solvent (DES)

h, hours. RT, room temperature. SSC, saturated sodium chloride. AcOH, acetic acid. PTM, post-translational modifications. FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting
Fortmann SD, Frey BF, Hanumanthu VS, Liu S, Goldsborough A, Kilchrist KV, Ferrell PB, Weaver CT, Grant MB, Welner RS. (2023) Fixation Before Dissociation Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent Preserves In Vivo States and Phospho-Signaling in Single-Cell Sequencing. bioRXiv [online preprint]. [abstract]