Spatial sequencing methods increasingly gain popularity within RNA biology studies. State-of-the-art techniques quantify messenger RNA expression levels from tissue sections and at the same time register information about the original locations of the molecules in the tissue. The resulting data sets are processed and analyzed by accompanying software that, however, is incompatible across inputs from different technologies.
Researchers at the Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine have developed spacemake, a modular, robust, and scalable spatial transcriptomics pipeline built in Snakemake and Python. Spacemake is designed to handle all major spatial transcriptomics data sets and can be readily configured for other technologies. It can process and analyze several samples in parallel, even if they stem from different experimental methods. Spacemake’s unified framework enables reproducible data processing from raw sequencing data to automatically generated downstream analysis reports. Spacemake is built with a modular design and offers additional functionality such as sample merging, saturation analysis, and analysis of long reads as separate modules. Moreover, spacemake employs novoSpaRc to integrate spatial and single-cell transcriptomics data, resulting in increased gene counts for the spatial data set. Spacemake is open source and extendable, and it can be seamlessly integrated with existing computational workflows.
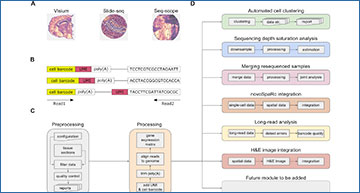
Overview of Spacemake
(A) Spacemake can handle inputs from different spatial transcriptomics technologies. (B) Spacemake is able to handle any barcode strategy. Cell barcode and unique molecular identifier (UMI) lengths are variable, and their position can be on either read. (C) Preprocessing, qualuty control, and processing steps. Each sample is processed the same way, regardless of the input type. (D) Spacemake is modular and extendable. Each module is implemented with a separate set of rules and commands, and everything is assembled in a top-level Snakefile.
Availability – Spacemake is freely available and can be found on GitHub: https://github.com/rajewsky-lab/spacemake
Sztanka-Toth TR, Jens M, Karaiskos N, Rajewsky N. (2022) Spacemake: processing and analysis of large-scale spatial transcriptomics data. Gigascience 1:giac064. [article]