Understanding the distinct gene sets and subpopulations within heterogeneous cell populations is essential for unraveling the complexities of biological systems. Recent advancements in computational pipelines have revolutionized the analysis of single-cell RNA and ATAC sequencing data, providing researchers with powerful tools to dissect cellular heterogeneity.
Researchers at Duke University have developed SifiNet, is a robust and accurate computational pipeline designed to identify gene sets, extract cellular subpopulations, and elucidate intrinsic relationships among these subpopulations. What sets SifiNet apart is its unique approach that bypasses the conventional cell clustering stage, a common step in many cellular annotation pipelines. By doing so, SifiNet avoids potential inaccuracies in clustering that may compromise subsequent analyses, ensuring more precise results.
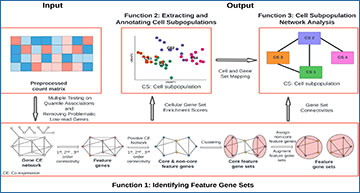
SifiNet pipeline
SifiNet takes the preprocessed feature count matrix as input, and uses gene co-expression network topology to identify feature gene sets (function 1). The identified feature gene sets are used to annotate cells (function 2), and the gene co-expression network is also used to reveal cell subpopulations’ transition or developmental relationships (function 3). The bottom row illustrates the main steps for identifying feature gene sets. After multiple testing on quantile associations and removing problematic low-read-count genes, SifiNet obtains a large gene co-expression network. Then, based on the 1st, 2nd and 3rd order connectivities, SifiNet identifies feature genes marked as red nodes. Then, SifiNet focuses on the positive co-expression network among feature genes and their node topologies to identify core feature genes, marked as blue nodes; the non-core features are marked in yellow. Next, SifiNet clustered the core feature genes into different clusters, and then assigned non-core feature genes and multi-role feature genes to the corresponding clusters. Finally, SifiNet obtains multiple feature gene sets.
The superiority of SifiNet has been demonstrated across multiple experimental datasets, showcasing its remarkable performance compared to other state-of-the-art methods. This pipeline excels in accurately identifying and annotating cellular subpopulations, providing researchers with valuable insights into the intricate landscape of cellular diversity.
One of the key strengths of SifiNet is its versatility. Unlike some existing methods that focus solely on single-cell RNA sequencing data, SifiNet can analyze both single-cell RNA and ATAC sequencing data. This comprehensive multi-omic approach enables researchers to obtain a more holistic understanding of cellular profiles, shedding light on both gene expression and chromatin accessibility.
Moreover, SifiNet is conveniently available as an open-source R package, making it easily accessible to researchers worldwide. This accessibility ensures that the benefits of SifiNet can be leveraged by a wide range of scientists, from seasoned bioinformatics experts to those new to the field.
SifiNet represents a significant advancement in the field of computational biology, offering researchers a powerful tool for analyzing cellular heterogeneity and multi-omic data. By providing accurate identification of gene sets and cellular subpopulations, SifiNet empowers researchers to uncover the intricate relationships within biological systems. With its robust performance and user-friendly interface, SifiNet is poised to drive further discoveries in cellular biology and beyond.
Availability – https://github.com/jichunxie/sifinet
Gao Q, Ji Z, Wang L, Owzar K, Li QJ, Chan C, Xie J. (2024) SifiNet: a robust and accurate method to identify feature gene sets and annotate cells. Nucleic Acids Res [Epub ahead of print]. [article].