Single-cell nanopore sequencing of full-length mRNAs transforms single-cell multi-omics studies. However, challenges include high sequencing errors and dependence on short-reads and/or barcode whitelists. To address these, researchers at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine have developed scNanoGPS to calculate same-cell genotypes (mutations) and phenotypes (gene/isoform expressions) without short-read nor whitelist guidance. The researchers apply scNanoGPS onto 23,587 long-read transcriptomes from 4 tumors and 2 cell-lines. Standalone, scNanoGPS deconvolutes error-prone long-reads into single-cells and single-molecules, and simultaneously accesses both phenotypes and genotypes of individual cells. Their analyses reveal that tumor and stroma/immune cells express distinct combination of isoforms (DCIs). In a kidney tumor, they identified 924 DCI genes involved in cell-type-specific functions such as PDE10A in tumor cells and CCL3 in lymphocytes. Transcriptome-wide mutation analyses identified many cell-type-specific mutations including VEGFA mutations in tumor cells and HLA-A mutations in immune cells, highlighting the critical roles of different mutant populations in tumors. Together, scNanoGPS facilitates applications of single-cell long-read sequencing technologies.
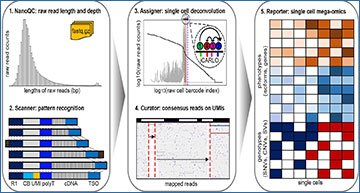
Schematic diagrams of scNanoRNAseq and scNanoGPS workflows
a Experimental workflow and library structure of scNanoRNAseq. b Computational workflow of scNanoGPS.
Availability – Software is available at GitHub: https://github.com/gaolabtools/scNanoGPS
Shiau CK, Lu L, Kieser R, Fukumura K, Pan T, Lin HY, Yang J, Tong EL, Lee G, Yan Y, Huse JT, Gao R. (2023) High throughput single cell long-read sequencing analyses of same-cell genotypes and phenotypes in human tumors. Nat Commun 14(1):4124. [article]