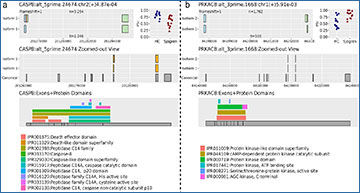
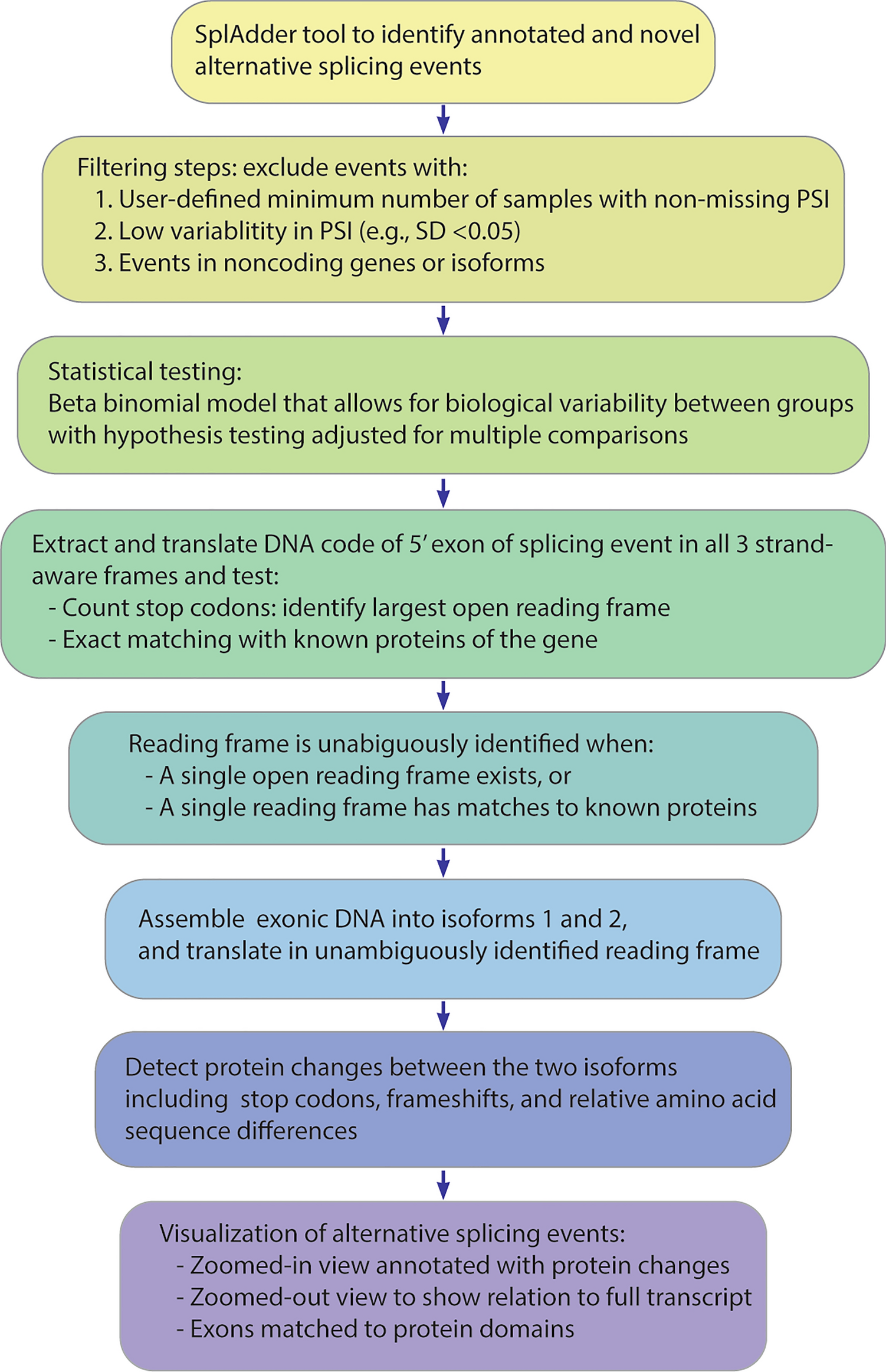
To understand the biological impact of alternative pre-mRNA splicing, it is vital to know which exons are involved, what protein domains they encode, and how the translated isoforms differ. Therefore, researchers at the University of Washington have developed a computational pipeline (RiboSplitter) focused on functional effect prediction. It builds on event-based alternative splicing detection with additional filtering steps leading to more efficient statistical testing, and with detection of isoform-specific protein changes. A key methodological advance is reading frame prediction by translating exonic DNA in all possible frames, then finding a single open reading frame, or a single frame with matches to known proteins of the gene. This allowed unambiguous translation in 93.9% of alternative splicing events when tested on RNA-sequencing data of B cells from Sjögren’s syndrome patients. RiboSplitter does not depend on reference annotations and translates events even when one or both isoform(s) are novel (unannotated). RiboSplitter’s visualizations illustrate each event with translation outcomes, show event location within the gene, and align exons to protein domains.
Flowchart of RiboSplitter analysis pipeline. PSI = Percent-spliced in
Availability – RiboSplitter’s code is publicly available at https://github.com/R-Najjar/RiboSplitter.
Najjar R, Mustelin T. (2023) Prediction of alternative pre-mRNA splicing outcomes. Sci Rep 13(1):20000. [article]