HLA typing provides essential results for stem cell and solid organ transplants, as well as providing diagnostic benefits for various rheumatology, gastroenterology, neurology, and infectious diseases. It is becoming increasingly clear that understanding the expression of patient HLA transcripts can provide additional benefits for many of these same patient groups. Researchers at UNC Health evaluated this study cohort using a long-read RNA sequencing methodology to provide rapid HLA genotyping results and normalized HLA transcript expression. This assay used NGSEngine to determine the HLA genotyping result and normalized mRNA transcript expression using Athlon2. The assay demonstrated an excellent concordance rate of 99.7%. Similar to previous studies, for the class I loci, patients demonstrated significantly lower expression of HLA-C than HLA-A and -B (Mann–Whitney U, p value = 0.0065 and p value = 0.0154, respectively). In general, the expression of class II transcripts was lower than that of class I transcripts. This study demonstrates a rapid high-resolution HLA typing assay using RNA-Seq that can provide accurate HLA genotyping and HLA allele-specific transcript expression in 7–8 h, a timeline short enough to perform the assay for deceased donors.
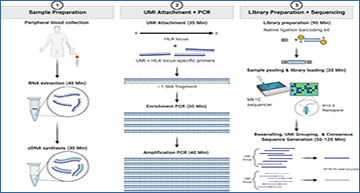
Patient sample workflow for RNA isolation, library preparation, and resultant HLA typing as described based on consensus sequence generation. In short, total RNA was isolated from peripheral blood, and a portion of the total RNA was purified. RNA fragmentation and quantitation were determined, and an RNA integrity number (RIN) was calculated for each sample. cDNA synthesis was then performed, after which PCR amplification and purification were utilized to achieve the final enriched HLA-locus specific UMI tagged amplicon. The HLA gene-specific amplicons for each patient were then used for library preparation and bar coding with the Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) platform. Sequencing was performed using the MinION R10.3 Flow Cell and loaded on the MinION Mk1C using the high-accuracy base calling module. The NGSengine bioinformatics pipeline was then utilized to provide HLA typing and Athlon2 was used to generate HLA allele-specific UMI counts.
Cornaby C, Montgomery MC, Liu C, Weimer ET. (2022) Unique Molecular Identifier-Based High-Resolution HLA Typing and Transcript Quantitation Using Long-Read Sequencing. Front Genet [Epub ahead of print]. [article]