Expression levels of microRNAs (miRNAs) in single cells are low and conventional miRNA detection methods require amplification that can be complex, time-consuming, costly and may bias results. Single cell microfluidic platforms have been developed; however, current approaches are unable to absolutely quantify single miRNA molecules expressed in single cells.
Researchers at the Imperial College London have developed an amplification-free sandwich hybridisation assay to detect single miRNA molecules in single cells using a microfluidic platform that optically traps and lyses individual cells. Absolute quantification of miR-21 and miR-34a molecules was achieved at a single cell level in human cell lines and validated using real-time qPCR. The sensitivity of the assay was demonstrated by quantifying single miRNA molecules in nasal epithelial cells and CD3+ T-cells, as well as nasal fluid collected non-invasively from healthy individuals. This platform requires ~50 cells or ~30 µL biofluid and can be extended for other miRNA targets therefore it could monitor miRNA levels in disease progression or clinical studies.
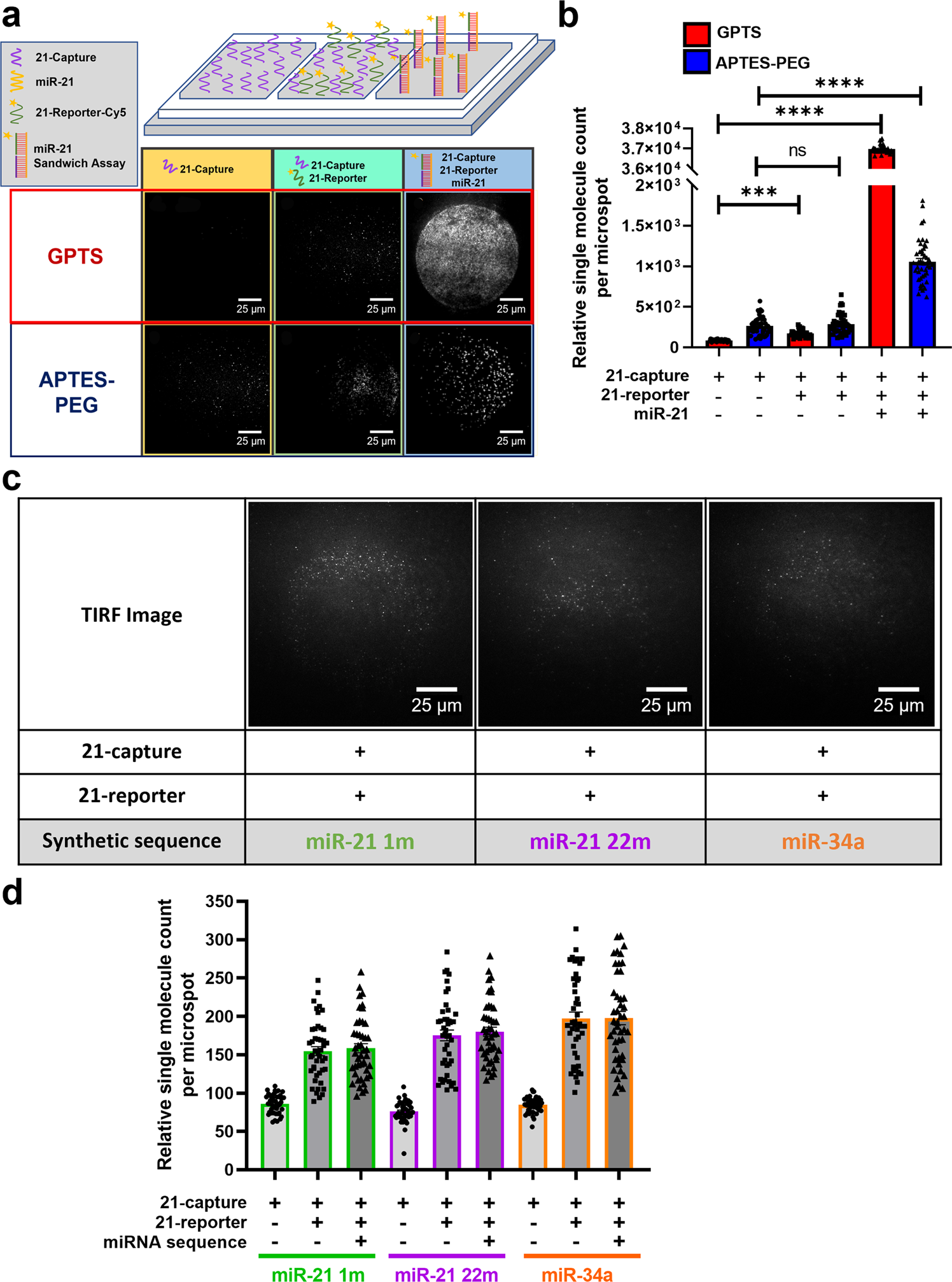
MiR-21 assay development
a Schematic diagram of an open chip platform consisting of three wells comparing GPTS (Red) and APTES-PEG (Blue) passivated surfaces: first well with 21-capture probe, second well with 21-capture and 21-reporter probes, and third well containing 1.2 ×106 molecules/nL miR-21 sequences with 21-capture and 21-reporter probes. TIRF images show single molecule binding events taking place on GPTS and APTES-PEG functionalised surface within the open chip. b Bar graph of single miR-21 molecules detected using the 21-capture microarrayed spots within the open chip. Open chips were incubated and imaged every 10 min for 2 h. Data are presented as individual points and mean ± SEM analysed by Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dunns ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001. c Raw TIRF images of microarrayed spots showing negligible single molecule binding of 21-capture and 21-reporter with miR-21 single-base modification at position 1 (miR-21 1m), 22 (miR-21 22m) and miR-34a. d Bar graph of relative single molecule count detected on 21-capture microarrayed spots in an open chip device with miR-21 1 m (green), mir-21 22m (purple) and miR-34a (orange) sequences present in individual wells. Open chips were incubated and imaged every 10 min for 2 h. Data are presented as individual points and mean ± SEM.
Ho V, Baker JR, Willison KR. et al. (2023) Single cell quantification of microRNA from small numbers of non-invasively sampled primary human cells. Commun Biol 6, 458. [article]