Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology has emerged as a powerful tool, allowing scientists to peer into the inner workings of cells with unprecedented resolution. By analyzing gene expression profiles at the single-cell level, researchers can glean insights into cell development, differentiation, and functional heterogeneity.
While scRNA-seq has revolutionized our understanding of cellular dynamics, one area that has received less attention is the analysis of multi-timepoint data. Understanding how gene expression changes over time is crucial for deciphering complex biological processes, such as development and disease progression. However, existing analytical frameworks for scRNA-seq often overlook the temporal dimension.
Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed CASi, a comprehensive framework designed specifically for analyzing multi-timepoint scRNA-seq data. CASi stands for Comprehensive Analysis of Single-cell data across multiple timepoints. It’s a cutting-edge framework developed to address the unique challenges posed by multi-timepoint scRNA-seq data.
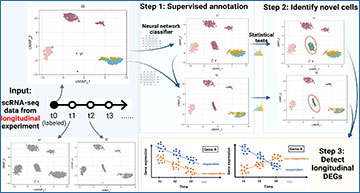
An overview of the CASi framework
The input is scRNA-seq data from different timepoints’ experiments. CASi mainly consists of three steps: (1) cross-time points cell annotation, (2) detection of potential novel cell types, (3) identification of temporal differentially expressed genes.
The key features that CASi offers:
- Cross-Timepoint Cell Annotation: CASi enables researchers to annotate cells across multiple timepoints, allowing for seamless comparison and tracking of cell populations over time. By accurately identifying cells at different timepoints, researchers can gain insights into the dynamic changes occurring within cell populations.
- Detection of Novel Cell Types: One of the most exciting aspects of CASi is its ability to detect potentially novel cell types that emerge over time. By analyzing changes in gene expression patterns across timepoints, CASi can uncover hidden cell subpopulations that may have gone unnoticed using traditional analytical methods.
- Visualization of Cell Population Evolution: CASi provides powerful visualization tools that allow researchers to explore the evolution of cell populations over time. From dynamic trajectory plots to interactive heatmaps, CASi offers intuitive visualizations that bring temporal dynamics to life.
- Identification of Temporal Differentially Expressed Genes (tDEGs): Another highlight of CASi is its ability to identify temporal differentially expressed genes (tDEGs). By pinpointing genes that exhibit significant changes in expression over time, CASi helps researchers uncover key drivers of temporal dynamics in gene expression.
CASi represents a significant advancement in the field of single-cell RNA sequencing analysis. By offering a comprehensive framework for analyzing multi-timepoint scRNA-seq data, CASi empowers researchers to unravel the temporal dynamics of gene expression with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. As our understanding of cellular biology continues to evolve, tools like CASi will play a crucial role in unlocking the mysteries of gene regulation and cellular behavior.
Wang Y, Flowers CR, Wang M, Huang X, Li Z. (2024) CASi: A framework for cross-timepoint analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data. Sci Rep 14(1):10633. [article]