Researchers from the University of California Santa Cruz have developed and benchmarked Mandalorion v4.1 for the identification and quantification of full-length transcriptome sequencing reads. It further improves upon the already strong performance of Mandalorion v3.6 used in the LRGASP consortium challenge. By processing real and simulated data, the researchers show three main features of Mandalorion: first, Mandalorion-based isoform identification has very high precision and maintains high recall even in the absence of any genome annotation. Second, isoform read counts as quantified by Mandalorion show a high correlation with simulated read counts. Third, isoforms identified by Mandalorion closely reflect the full-length transcriptome sequencing data sets they are based on.
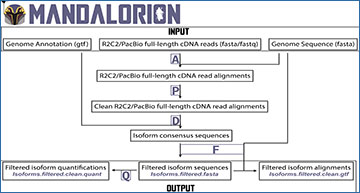
Mandalorion workflow
Input files, processing steps, and output files are shown in a workflow diagram. Using several modules (A, P, D, F, and Q), Mandalorion aligns reads to a genome sequence (using minimap2), groups reads into isoforms based on those alignments, and generates a consensus sequence for each isoform (using pyabpoa). It then aligns these isoform sequences (using minimap2) and filters the isoforms based on those alignments
Availability – Mandalorion is available at https://github.com/christopher-vollmers/Mandalorion under the MIT license.
Volden R, Schimke KD, Byrne A, Dubocanin D, Adams M, Vollmers C. (2023) Identifying and quantifying isoforms from accurate full-length transcriptome sequencing reads with Mandalorion. Genome Biol 24(1):167. [article]