The main critical step in single-cell transcriptomics is sample preparation. Several methods have been developed to preserve cells after dissociation to uncouple sample handling from library preparation. Yet, the suitability of these methods depends on the cell types to be processed. In this project, researchers at the Bellvitge Institute for Biomedical Research performed a systematic comparison of preservation methods for droplet-based single-cell RNA-seq on neural and glial cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Their results show that while DMSO provides the highest cell quality in terms of RNA molecules and genes detected per cell, it strongly affects the cellular composition and induces the expression of stress and apoptosis genes. In contrast, methanol fixed samples display a cellular composition similar to fresh samples and provide a good cell quality and little expression biases. Taken together, these results show that methanol fixation is the method of choice for performing droplet-based single-cell transcriptomics experiments on neural cell populations.
Experimental Setup
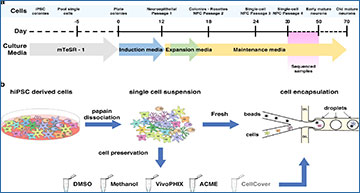
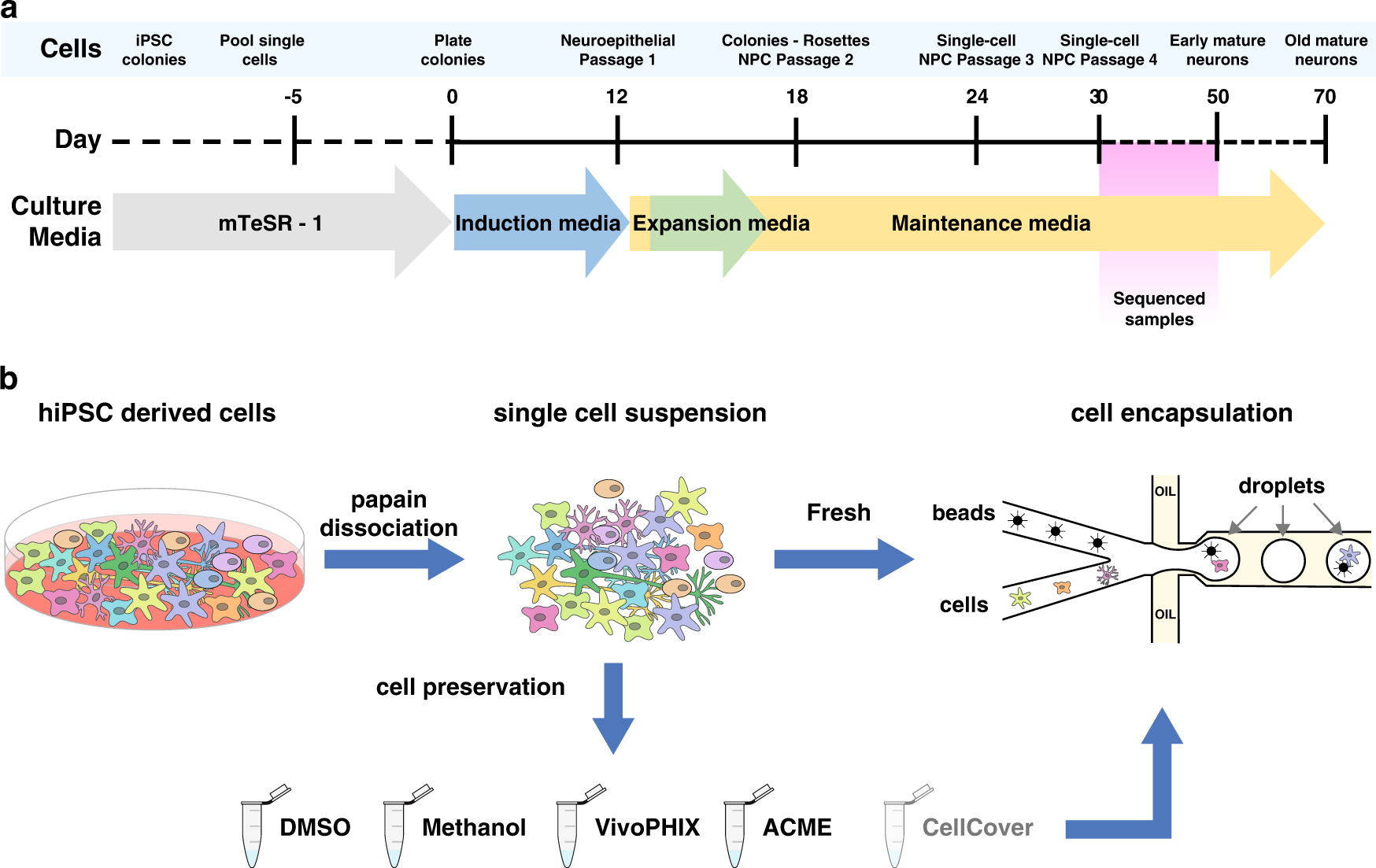
a Schematic representation of the differentiation protocol of hiPSCs to neural progenitor cells. b Systematic comparison of preservation methods. After the differentiation of hiPSCs, all cells were dissociated using papain-accutase and either directly encapsulated or preserved using one of the different reagents tested. After being preserved, cells were thawed or rehydrated and encapsulated using a commercial Drop-seq setup using the same protocols.
Gutiérrez-Franco A, Ake F, Hassan MN, Cayuela NC, Mularoni L, Plass M. (2023) Methanol fixation is the method of choice for droplet-based single-cell transcriptomics of neural cells. Commun Biol 6(1):522. [article]