Researchers at Biofidelity have developed a low-cost, simple and rapid assay for single-molecule detection of multiple gene fusions from RNA. Detecting these fusions faster and at a lower cost has the potential to revolutionize patient care and make precision medicine globally accessible to more people.
Published online in BMC Medical Genomics, a new study expands on a previous scientific report introducing the technology and details the RNA capabilities of ASPYRE®, which can analyze DNA and RNA concurrently from a single patient sample. Biofidelity has initially developed the novel assay for single-molecule detection of multiple gene fusions for non-small cell lung cancer patients (NSCLC).
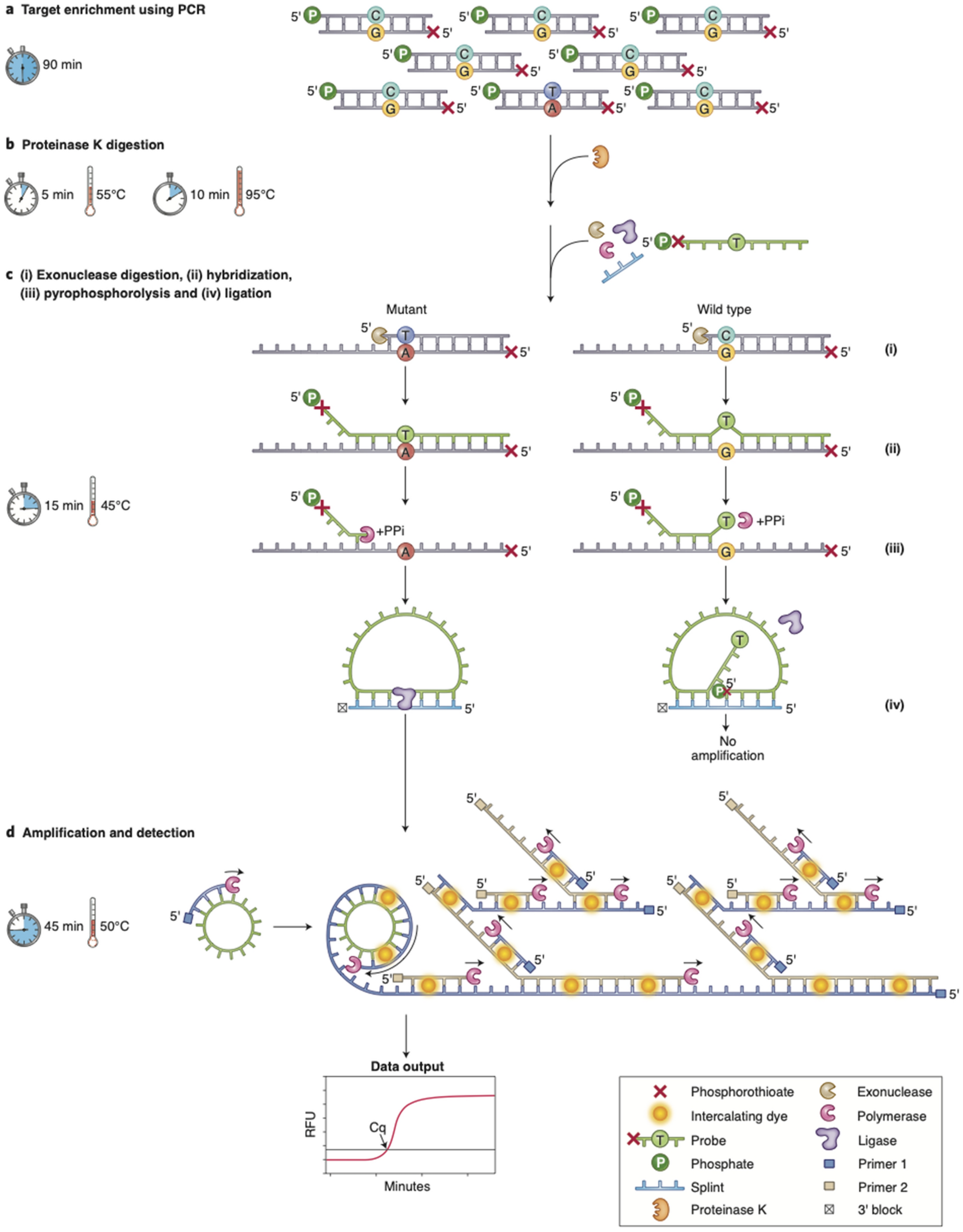
Overview of the ASPYRE assay
(a) Multiplex PCR amplification of wild-type and mutant alleles. (b) Enzymatic digestion of the PCR enzyme and subsequent heat-inactivation. (c) Exonuclease digestion to create single-stranded target molecules; hybridization of oligonucleotide probes to both mutant and wild-type sequences, with a mismatch to the wild-type sequence at the site of mutation; and pyrophosphorolysis of hybridized probes. (d) Circularization of only those probes that have been digested beyond the mutation site; and isothermal amplification and detection of circularized probes. Artwork by Debbie Maizels, Zoobotanica Scientific Illustration.
“RNA is an under-utilized but critical tool for oncology,” said Biofidelity CMO Dr. Wendy Levin. “We have demonstrated that our technology provides ultra-sensitive detection of multiple gene fusions directly from RNA concurrently, ensuring that no patient misses out on the promise of precision medicine.”
Today, there are more than ten effective targeted therapies available to treat NSCLC patients whose tumor harbors a gene fusion. These targeted treatments offer an alternative to chemotherapy regimens, often with less harsh side effects and better results. Five-year survival rates for lung cancer have tripled since targeted therapies became available in 2010.
Some currently available next generation sequencing assays target large genomic regions in DNA where translocations occur and, when abnormalities are detected, infer that they lead to the production of RNA fusions. This strategy can result in as many as 25% of fusions being missed. Missed fusions mean that a significant number of patients will not receive the targeted therapy that is likely to provide them with the most benefit.
“Our breakthrough technology, ASPYRE, fits into the underserved space between NGS and PCR testing enabling fast clinical decision-making through simple, precise, and targeted identification of panels of genomic biomarkers,” said paper co-author Dr. Barnaby Balmforth, Biofidelity Co-founder and CEO. “ASPYRE makes genomic data more accessible and easier to interpret, helping to ensure that all patients, globally, have the information needed to receive the right treatment at the right time.”
While several RNA specific next generation sequencing panels are now available, they can cost as much as $5,000 in additional testing. Conversely, ASPYRE technology offers a low-cost panel for all actionable genes in NSCLC and the ability to return results in as little as two days.
In addition to effectively identifying gene fusions from RNA, ASPYRE employs readily available PCR instrumentation to run its innovative diagnostic testing, yet its dramatically simplified workflow integrates easily into existing laboratory workflows.
Source – PRNewswire
Gray ER, Mordaka JM, Christoforou ER, von Bargen K, Potts ND, Xyrafaki C, Silva AL, Stolarek-Januszkiewicz M, Anton K, Powalowska PK, Andreazza S, Tomassini A, Palmer RN, Cooke A, Osborne RJ, Balmforth BW. (2022) Ultra-sensitive molecular detection of gene fusions from RNA using ASPYRE. BMC Med Genomics 15(1):215. [article]