The recent advances in spatial transcriptomics have brought unprecedented opportunities to understand the cellular heterogeneity in the spatial context. However, the current limitations of spatial technologies hamper the exploration of cellular localizations and interactions at single-cell level. Researchers at Tongji University have developed spatial transcriptomics deconvolution by topic modeling (STRIDE), a computational method to decompose cell types from spatial mixtures by leveraging topic profiles trained from single-cell transcriptomics. STRIDE accurately estimated the cell-type proportions and showed balanced specificity and sensitivity compared to existing methods. The researchers demonstrated STRIDE’s utility by applying it to different spatial platforms and biological systems. Deconvolution by STRIDE not only mapped rare cell types to spatial locations but also improved the identification of spatially localized genes and domains. Moreover, topics discovered by STRIDE were associated with cell-type-specific functions and could be further used to integrate successive sections and reconstruct the three-dimensional architecture of tissues. Taken together, STRIDE is a versatile and extensible tool for integrated analysis of spatial and single-cell transcriptomics.
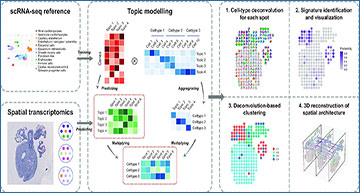
Schematic representation of the STRIDE workflow
First, STRIDE estimates the gene-by-topic distribution and the topic-by-cell distribution from scRNA-seq. The topic-by-cell distribution is then summarized to the cell-type-by-topic distribution by Bayes’ Theorem. Next, the pre-trained topic model is applied to infer the topic distributions of each location in spatial transcriptomics. By combining cell-type-by-topic distribution and topic-by-location distribution, the cell-type fractions of each spatial location could be inferred. STRIDE also provides several downstream analysis functions, including signature detection and visualization, spatial domain identification and reconstruction of spatial architecture from sequential ST slides of the same tissue.
Availability – STRIDE is publicly available at https://github.com/wanglabtongji/STRIDE
Sun D, Liu Z, Li T, Wu Q, Wang C. (2022) STRIDE: accurately decomposing and integrating spatial transcriptomics using single-cell RNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 50(7):e42. [article]