Understanding the genetic mutations that drive cancer is crucial for developing targeted treatments and improving patient outcomes. Traditionally, scientists have relied on DNA sequencing (DNA-seq) to identify somatic mutations (SMs) in cancer genomes. However, recent advancements have shown that RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) can also be a powerful tool in this area. In an exciting development, researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago have created a machine learning-based pipeline to discover somatic mutations using RNA-seq data, leading to significant new insights into the mutational landscape of various cancers.
What Are Somatic Mutations?
Somatic mutations are changes in the DNA that occur after conception and can be found in any of the body’s cells except the germ cells (sperm and egg). These mutations can drive the development and progression of cancer by altering the normal functions of genes involved in cell growth and division.
The Power of RNA Sequencing
RNA-seq is a technique that sequences the RNA in a cell, providing a snapshot of the actively transcribed genes. While DNA-seq looks at the entire genome, RNA-seq focuses on the parts of the genome that are being actively used by the cell. This approach can reveal mutations in the transcribed part of the genome, which are directly involved in the production of proteins.
The New RNA-SMs Pipeline
Researchers have developed a new pipeline, called RNA-SMs, which uses machine learning to identify somatic mutations from RNA-seq data. This innovative method was applied to data from over 8,000 tumor samples in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), a comprehensive public database of cancer genetics.
Discovery of Novel Mutations
Using the RNA-SMs pipeline, the researchers identified over 105,000 new somatic mutations that had not been reported in previous TCGA studies. These novel mutations have important implications for cancer treatment, as they can help scientists design more precise and effective targeted therapies.
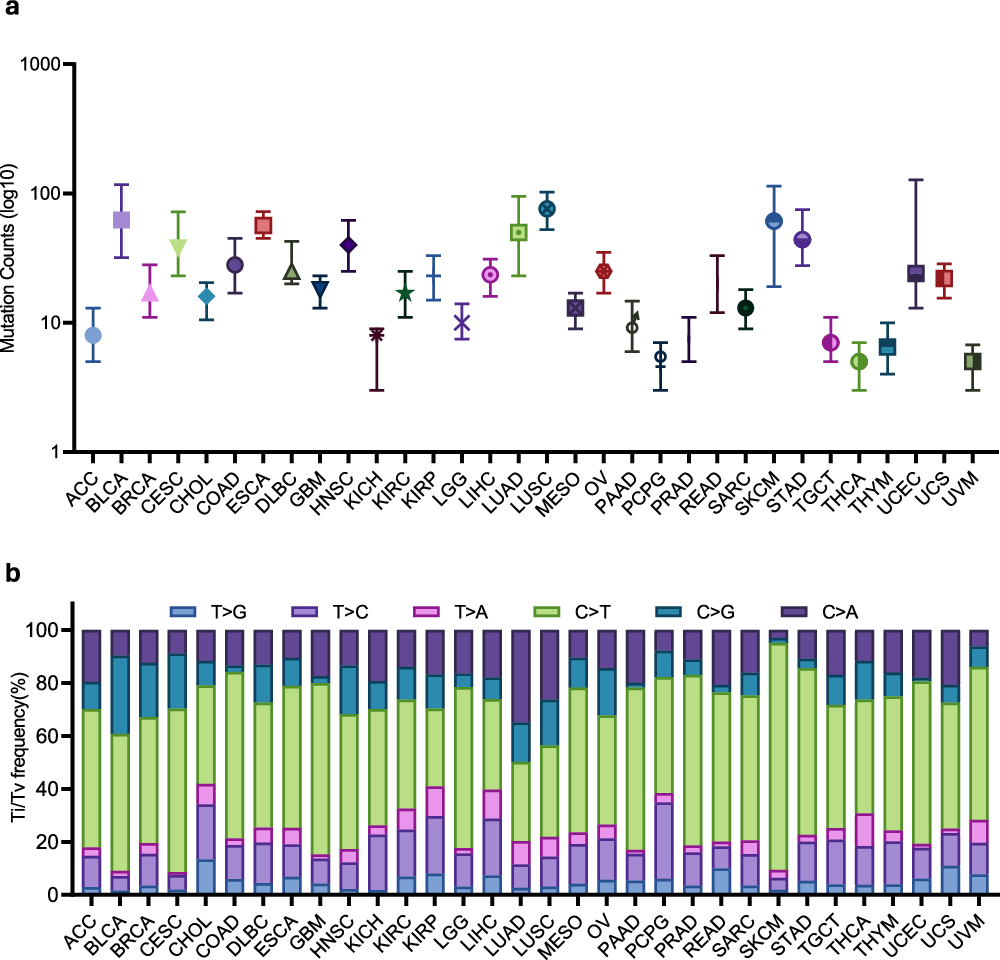
Pan-cancer RNA-SM profiles in TCGA
a Distribution of RNA-SM counts in individual patients across 32 types of cancer. b Composition of allele transition frequency in RNA-SMs across 32 types of cancer.
Combining DNA-Seq and RNA-Seq Data
To provide a more comprehensive view of cancer mutations, the researchers combined the somatic mutations identified by both RNA-seq and DNA-seq. This combined analysis covers 32 different types of cancer, offering a detailed and updated mutational landscape.
Introducing OncoDB: A New Online Resource
The results of this extensive analysis are now available in a new online database called OncoDB (https://oncodb.org). OncoDB provides researchers, clinicians, and anyone interested in cancer genetics with a comprehensive resource to explore gene mutations across various cancer types. This tool can help in understanding the genetic basis of cancer and in the development of new treatment strategies.
Implications for Cancer Treatment
The discovery of these novel somatic mutations through RNA-seq represents a significant advancement in cancer research. By identifying mutations that were previously undetectable, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the genetic factors that drive cancer. This knowledge is crucial for developing targeted therapies that can more effectively combat the disease and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The integration of RNA-seq with traditional DNA-seq methods opens up new possibilities in cancer research. The RNA-SMs pipeline and the OncoDB database represent major steps forward in our ability to identify and understand the mutations that underlie cancer. As research continues to build on these findings, we can look forward to more personalized and effective treatments for cancer patients, bringing hope to millions worldwide.
Availability – All source code and instruction for the IMAPR pipeline is available through GitHub (https://github.com/wang-lab/IMAPR),
Tang G, Liu X, Cho M et al. (2024) Pan-cancer discovery of somatic mutations from RNA sequencing data. Commun Biol [Epub ahead of print]. [article]