Sophisticated methods to properly pre-process and analyze the increasing collection of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data are increasingly being developed. On the contrary, the best practices to integrate these data into metabolic networks, aiming at describing metabolic phenotypes within a heterogeneous cell population, have been poorly investigated. In this regard, a critical factor is the presence of false zero values in reactions essential for a fundamental metabolic function, such as biomass or energy production. Researchers from the University of Milano-Bicocca have investigated the role of denoising strategies in mitigating this problem.
The researchers applied state-of-the-art denoising strategies – namely MAGIC, ENHANCE, and SAVER – on three public scRNA-seq datasets. They then associated a metabolic flux distribution with every single cell by embedding its noise-free transcriptomics profile in the constraints of the optimization of a core metabolic model. Finally, they used the obtained single-cell optimal metabolic fluxes as features for cluster analysis. The researchers compared the results obtained with different techniques, and with or without the use of denoising. They also investigated the possibility of applying denoising directly on the Reaction Activity Scores, which are metabolic features extracted from the read counts, rather than on the read counts.
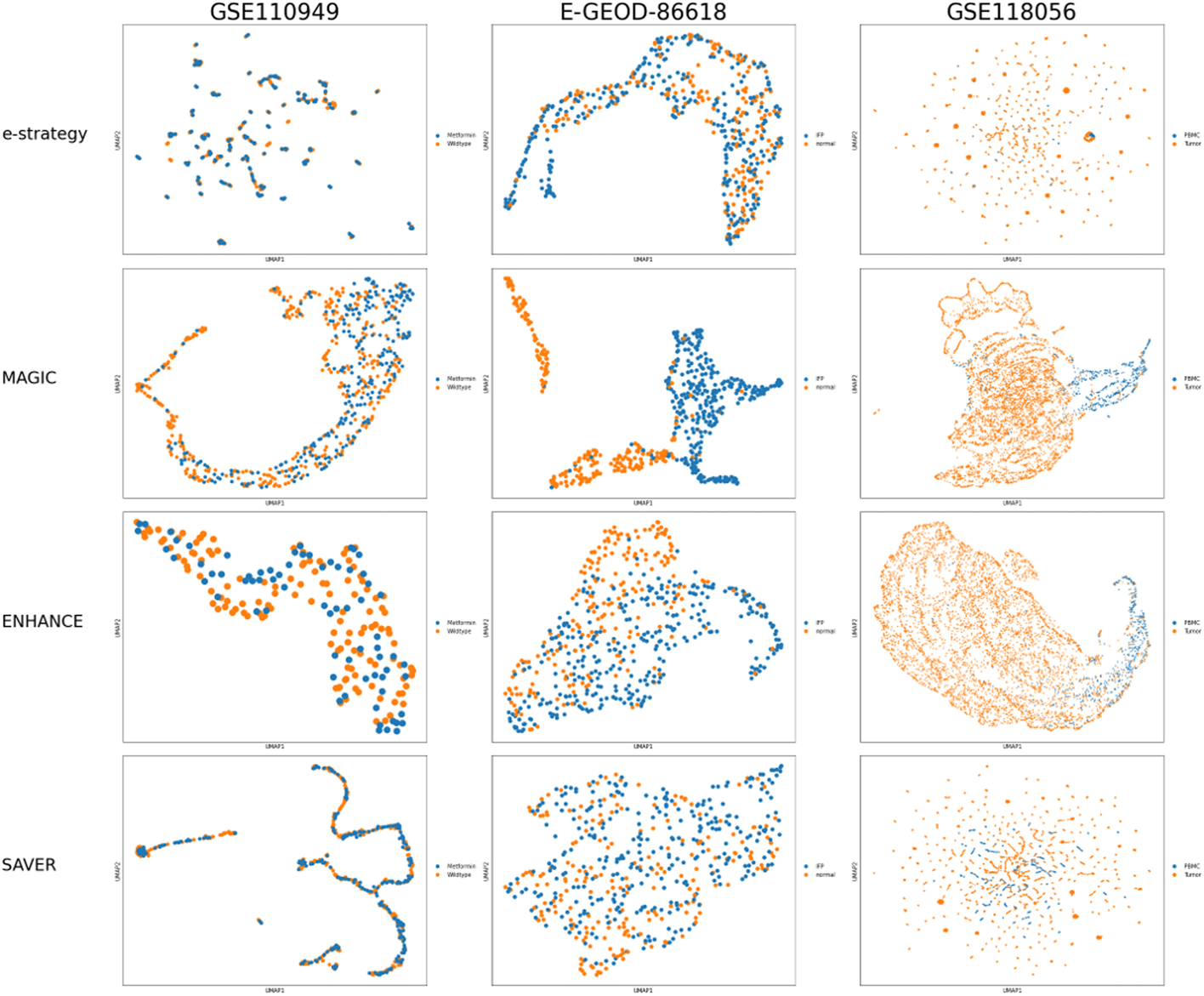
These researchrs show that denoising of transcriptomics data improves the clustering of single cells. They also illustrate that denoising restores important metabolic properties, such as the correlation between cell cycle phase and biomass accumulation, and between the RAS scores of reactions belonging to the same metabolic pathway. They show that MAGIC performs better than ENHANCE and SAVER, and that, denoising applied directly on the RAS matrix could be an effective alternative in removing false zero values from essential metabolic reactions.
Flux cluster analysis
The results are embedded in a two-dimensional graph using UMAP and coloured using the a priori knowledge. Each column represents a different dataset, and each row a different denoising strategy applied on the read counts matrix before the computation of the RAS matrix
These results indicate that including denoising as a pre-processing operation represents a milestone to integrate scRNA-seq data into Flux Balance Analysis simulations and to perform single-cell cluster analysis with a focus on metabolic phenotypes.
Galuzzi BG, Vanoni M, Damiani C. (2022) Combining denoising of RNA-seq data and flux balance analysis for cluster analysis of single cells. BMC Bioinformatics 23(Suppl 6):445. [article]